Table of Contents
Indigo Scripting Tutorial
Talking to the Indigo Server
The Indigo Plugin Host (IPH) provides a python scripting and plugin environment, which makes controlling the Indigo Server easy via the high-level python language (the official python web site has great python tutorials). Every plugin automatically runs inside its own Indigo Plugin Host process, but you can also start the IPH in an interactive mode to directly communicate with the Indigo Server. It is a great way to experiment with Indigo's python environment, which is available to both python scripts run by Indigo and the plugin architecture. Want the ability to just put some Python scripts onto a menu somewhere for easy access? There's a simple way to do it.
To launch the Terminal utility application (inside /Applications/Utilities/) in an Indigo shell mode choose the Plugins→Open Scripting Shell menu item.
Note: you'll want to read through the introduction section of the Indigo Object Model, which gives you some fundamental information that you need to successfully script Indigo.
Example Code Snippets
Below are some sample scripts you can copy/paste directly into the IPH window (opened when following the directions above). Keep in mind, these are only examples, so be sure to read the full Indigo Object Model (IOM) Reference.
Note: For simplicity, some of the samples below specify objects based on name (“office desk lamp”). However, the preferred lookup mechanism is to use the object's ID which can be retrieved by control-clicking on the object's name in Indigo's Main Window. By using the ID, you ensure the object will be found even if its name is changed.
Device Examples
Turn on the device "office desk lamp":
indigo.device.turnOn(1234567890) # Preferred, where the number is the ID of "office desk lamp"
# OR the less preferred way because it will break if you rename the device
indigo.device.turnOn("office desk lamp")
Duplicate the device "office desk lamp":
indigo.device.duplicate(1234567890, duplicateName="office desk lamp2") # where the number is the ID of "office desk lamp"
In 4 seconds turn on the device "office desk lamp" for 2 seconds:
indigo.device.turnOn(1234567890, duration=2, delay=4) # where the number is the ID of "office desk lamp"
Turn off all devices:
indigo.device.allOff()
Count the number of device modules:
indigo.devices.len()
Count the number of dimmable device modules:
indigo.devices.len(filter="indigo.dimmer")
Count the number of devices defined by all of our plugin types:
indigo.devices.len(filter="self")
Count the number of irBlaster type devices defined by our plugin:
indigo.devices.len(filter="self.irBlaster")
Get the on state of a device if it has the onState property (uses Python's hasattr() introspection method):
lamp = indigo.devices[1234567890] # where the number is the ID of "office desk lamp"
if hasattr(lamp, 'onState'):
isOn = lamp.onState
Get the class of a device (uses Python's __class__ property):
lamp = indigo.devices[1234567890] # where the number is the ID of "office desk lamp"
if lamp.__class__ == indigo.DimmerDevice:
theBrightness = lamp.brightness
Turn on a light only if it's been off for longer than 1 minute:
from datetime import datetime
lamp = indigo.devices[91776575] # ID of "Hallway light"
timeDelta = datetime.now() - lamp.lastChanged
if not lamp.onState and timeDelta.seconds > 60:
indigo.device.turnOn(91776575) # ID of "Hallway light"
Access a custom device state
# get the device dev = indigo.devices[23989834] # Some custom device # access the state through the states property, use the key # that's displayed in the Custom States tile on the main window # when you have a custom device selected print(dev.states["someDeviceStateKey"]) # show all the device states: print(dev.states)
Variable Examples
Create a new Indigo variable named fooMonster, change its value multiple times, and delete it:
newVar = indigo.variable.create("fooMonster", "default value")
indigo.variable.updateValue(newVar, "asleep")
indigo.variable.updateValue(newVar, "awake")
indigo.variable.delete(newVar)
Getting a variable object and using it's value:
myVar = indigo.variables[123]
if myVar.value == "true":
indigo.server.log("The variable had a value of 'true'")
Duplicating a variable:
indigo.variable.duplicate("fooMonster", duplicateName="fooMonsterSister")
Using a variable value in an HTTP GET
import requests
my_var = indigo.variables[1893500335] # always use variable ID rather than name
query_args = {"param1": my_var.value}
reply = requests.get("http://example.com/foo/bar", params=query_args)
Setting a variable to Python types
Since Indigo variable values are always strings, you have to convert anything that's not a string. It's safest to use the str() method:
my_ascii_string = "ASCII String"
indigo.variable.updateValue(1234567, value=my_ascii_string)
my_unicode_string = "éçø"
indigo.variable.updateValue(1234567, value=my_unicode_string)
my_integer = 1
indigo.variable.updateValue(1234567, value=str(my_integer))
my_float = 1.0
indigo.variable.updateValue(1234567, value=str(my_float))
my_list = ["one", 2, "three", 4]
indigo.variable.updateValue(1234567, value=str(my_list))
my_dictionary = {"first":1, "second":"two", "third":3, "fourth":"four"}
indigo.variable.updateValue(1234567, value=str(my_dictionary))
Any Python object that can be converted to a string can then be inserted into an Indigo variable. Note: conversions of this type are often one way: you can't necessarily automatically recreate the Python object from the string created by the str() method. For primitive types like numbers it may work, but for complex Python types like lists and dictionaries it will not. If you want to use Indigo to store a string representation of some complex Python data types, you can use JSON to encode them into strings then later decode them back into their respective Python objects:
import json
my_list = ["one", 2, "three", 4]
my_dictionary = {"first":1, "second":"two", "third":3, "fourth":"four", "my_list": my_list}
indigo.variable.updateValue(1234567, value=json.dumps(my_dictionary))
# string will be something like: '{"second": "two", "myList": ["one", 2, "three", 4], "fourth": "four", "third": 3, "first": 1}'
my_new_dictionary = json.loads(indigo.variables[1234567].value)
#my_new_dictionary is now the same as my_dictionary
my_new_dictionary["my_list"]
# results in: ['one', 2, 'three', 4]
Custom Python classes that you create can implement the %%str(self)%% method. Take this simple example:
class myCustomClass:
def __init__(self):
self.a=1
self.b=2
def __str__(self):
outputString = f"a:{self.a}, b:{self.b}"
return outputString
If you have an instance of that class, then you can create a string representation of the class to insert into an Indigo variable:
cl = myCustomClass() indigo.variable.updateValue(1234567, value=str(cl)) # the value of the variable in Indigo will look like this: 'a:1, b:2' not including the quotes
For further information on Python classes, check out this great tutorial.
Date and Time Examples
Get the current server time:
indigo.server.getTime()
Calculate the sunset time in 1 week:
import datetime one_week = indigo.server.getTime().date() + datetime.timedelta(days=7) indigo.server.calculateSunset(one_week)
Action Group Examples
Execute Action Group 12345678:
indigo.actionGroup.execute(12345678)
Log Examples
Log to the Indigo Event Log window all of the attributes/properties of the device "office desk lamp":
lamp = indigo.devices["office desk lamp"]
indigo.server.log(f"{lamp.name}: \n{lamp}")
Log to the Indigo Event Log window using different levels of logging
import logging
indigo.server.log("info log message which will show in black text", level=logging.INFO)
indigo.server.log("warning log message which will show in orange text", level=logging.WARNING)
indigo.server.log("error log message which will show in red text", level=logging.ERROR)
# Equivalent of above server API calls that instead use the plugin instances default logger instance:
self.logger.info("info log message which will show in black text")
self.logger.warn("warning log message which will show in orange text")
self.logger.error("error log message which will show in red text")
Print the last 5 Event Log entries:
logList = indigo.server.getEventLogList(lineCount=5) print(logList)
Folder Examples
Iterate over a list of all device folders
for folder in indigo.devices.folders:
print(f"Folder id: {folder.id} name: {folder.name}, remoteDisplay: {folder.remoteDisplay}")
Create a trigger folder named "My Triggers" and, if it exists, just return the existing one
try:
myFolder = indigo.triggers.folder.create("My Triggers")
except ValueError as e:
if e.message == "NameNotUniqueError":
# a folder with that name already exists so just get it
myFolder = indigo.triggers.folders["My Triggers"]
else:
# you'll probably want to do something else to make myFolder a valid folder
myFolder = None
Make a folder visible in remote clients (IWS, Indigo Touch, etc.)
indigo.devices.folder.displayInRemoteUI(123, value=True)
Get the folder containing a device
lamp = indigo.devices["office desk lamp"]
# An object that's not in a folder will have a folder id of 0, which isn't a valid folder
# so we need to make sure it's a valid folder ID first
if lamp.folderId != 0:
lampsFolder = indigo.devices.folders[lamp.folderId]
else:
lampsFolder = None
Miscellaneous Examples
Get a list of all serial ports, excluding any Bluetooth ports:
indigo.server.getSerialPorts(filter="indigo.ignoreBluetooth")
Sending emails
# Simple Example
indigo.server.sendEmailTo("emailaddress@company.com", subject="Subject Line Here", body="Some longish text for the body of the email")
# Putting a variable's data into the subject and body
theVar = indigo.variables[928734897]
theSubject = f"The value of {theVar.name}"
theBody = f"The value of {theVar.name} is now {theVar.value}"
indigo.server.sendEmailTo("emailaddress@company.com", subject=theSubject, body=theBody)
# Putting device data into the subject and body
theDevice = indigo.devices[980532604]
theSubject = f"Summary of {theDevice.name}"
theBody = f"onState is {theDevice.onState}\n lastChanged is {theDevice.lastChanged}"
indigo.server.sendEmailTo("emailaddress@company.com", subject=theSubject, body=theBody)
Starting the host from an existing terminal window
If you already have a Terminal shell running, you can launch it directly. To start the IPH in interactive mode just execute the following inside the Terminal:
/usr/local/indigo/indigo-host
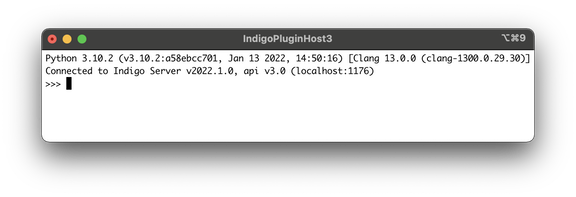
As shown, the IPH will automatically connect to the IndigoServer running on the same Mac and will show the server's version information and the Indigo Plugin Host Python version. Additionally, you'll notice that Indigo Server logs the connection of the interactive shell plugin. Add /usr/local/indigo/ to the PATH in your shell (in ~/.bashrc) and you won't have to specify the full path.
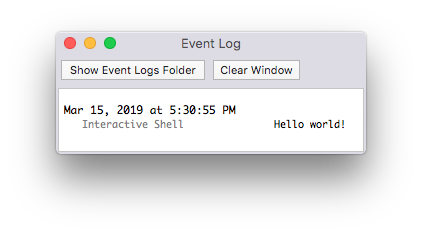
Next, let's tell the Indigo Server to log a message to the Event Log window (again, via the Terminal application):
indigo.server.log("Hello world!")
Connecting Remotely over SSH
If you have SSH configured so you can remotely connect to your Mac running the Indigo Server, then you can use SSH to start the IPH interactively anywhere using the syntax:
ssh username@indigo_mac_ipaddr -t /usr/local/indigo/indigo-host
What Else Can it Do?
The IPH gives you full access to the Indigo Object Model (IOM) providing access to create/edit/delete/control Indigo objects, as well as several Indigo utility functions, INSTEON device commands, and X10 device commands. Access to all of this functionality is provided by the indigo module automatically loaded and included in any python scripts run by the IPH (including interactive IPH sessions like we are using here).
Executing Indigo Commands Directly
In addition to communicating interactively with Indigo via the shell, you can also send direct python commands to Indigo via the IPH. For example, to get the current brightness of the device “office lamplinc”:
indigo-host -e 'return indigo.devices["office lamplinc"].brightness'
Or to toggle the device “office lamplinc” three times:
indigo-host -e '
indigo.device.toggle("office lamplinc")
indigo.device.toggle("office lamplinc")
indigo.device.toggle("office lamplinc")
'
Note when your commands are executed the indigo module is already loaded and connected and you can execute standard python code (loops, conditionals, etc.).
Caveat: Each call creates a new IPH (indigo-host) process which must establish a connection to the Indigo Server. Although this is relatively fast, calling it multiple times a second is not recommended.
Executing Indigo Python Files
The IPH can also be used to execute Indigo python (.py) files, like this:
indigo-host -x '/SomeFolder/indigo_script.py'
Caveat: Each call creates a new IPH (indigo-host) process which must establish a connection to the Indigo Server. Although this is relatively fast, calling it multiple times a second is not recommended.
Executing AppleScript
Often times, you may find yourself wanting to execute an AppleScript from Python. You want to send some parameters to the AppleScript and you want to get results back in some format. There's a pretty straight-forward way to do this that we've described in this wiki article.
This is a great pattern for calling AppleScripts from Python, specifically a great way to integrate other scriptable Mac app data with Indigo.
Shared Classes and Methods in Python Files (Python Modules)
You may install Python modules/libraries in a special location to make them available to Indigo scripts and plugins, but not to generic Python. This is particularly useful if the module/library includes references to the IOM (since it will only be loaded by processes that know about the indigo module). This location is:
/Library/Application Support/Perceptive Automation/Python3-includes
Any Python files in this directory that define methods and/or classes will be available to any Python script whenever the interpreter is loaded (note that it's the Library directory at the top level of your boot disk, not the one in your user folder). These are referred to as Python modules.
So, you can create files of classes, functions, etc. you want to share between all Python scripts using these mechanisms. If you add/change something in that directory while the Indigo Server is running, you'll need to tell the server to reload - select the Plugins→Reload Libraries and Attachments menu item and Indigo will restart the Python interpreter (which will cause your module to be reloaded).
Files added to the generic module location can also import the entire IOM - IF the script that's actually running is started by Indigo. Here's a simple script that you can use that will safely import the IOM and will show a specific error when used from a Python script that's not started by Indigo:
"""
indigo_attachments.py
In this file you can insert any methods and classes that you define.
They will be shared by all Python scripts - you can even import the
IOM (as shown below) but if you do then you'll only be able to import
this script in Python processes started by Indigo. If you don't need
the IOM then skip the import and it'll work in any Python script
no matter where it's run from.
"""
try:
import indigo
except ImportError:
print("The indigo module can only be used by scripts started from within Indigo")
raise ImportError
from datetime import datetime
def log(message, label=None):
# Create a log line with the date/timestamp prepended in MM/DD/YYYY HH:MM:SS format
log_line = f"{datetime.today().strftime('%x %X')} {message}"
# Write the log line with the label. If you didn't pass in a label
# then the default label will be used.
indigo.server.log(log_line, type=label)
Then, when you want to use any of the classes/methods in the file, just import the file and go:
import indigo_attachments
indigo_attachments.log("Here's a special sort of log message", label="My Custom Label")
What you'll see in the Event Log:
My Custom Label 01/15/16 10:20:39 Here's a special sort of log message
If you try to run this script in a normal python session, you'll see the print statement followed by the ImportError:
MyMac:testdir jay$ python2.7 testHandlerCall.py
The indigo module can only be used by scripts started from within Indigo
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "testHandlerCall.py", line 3, in <module>
import indigo_attachments
File "/Users/USERNAME/Library/Python/2.7/site-packages/indigo_attachments.py", line 14, in <module>
raise ImportError
ImportError
Scripting Indigo Plugins
Indigo plugins are also scriptable. Because plugin-defined devices look almost identical to built-in devices, you can get (but not set) state information from them (see device examples above for a lot of examples). You can also get some of the other properties for a plugin. Most importantly you can execute plugin-defined actions, which is how you'd set their state values.
The first step is to get an instance of the plugin:
iTunesId = "com.perceptiveautomation.indigoplugin.itunes" # supplied by the plugin's documentation iTunesPlugin = indigo.server.getPlugin(iTunesId)
This will always return to you a plugin object, defined with the following properties:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
compatibleUpdateAvailable | bool | True is there is a compatible update to the plugin available from the store |
includedWithServer | str | True if the plugin is included in the Indigo installer |
incompatibleUpdateAvailable | bool | True is there is an update to the plugin available from the store but that is incompatible with the Indigo Server version currently running |
latestCompatibleDownloadCount | int | The number of downloads from the plugin store of this specific version of the plugin (None if the plugin isn't in the plugin store) |
latestCompatibleDownloadURL | str | The URL for the latest compatible release from the plugin store (None if the plugin isn't in the plugin store) |
latestCompatibleReleaseDate | datetime | The date for the latest compatible release in the plugin store (None if the plugin isn't in the plugin store) |
latestCompatibleSummaryDesc | str | The summary for the latest compatible release in the plugin store (None if the plugin isn't in the plugin store) |
latestCompatibleVers | str | The version of the most recent compatible release (None if the plugin isn't in the plugin store) |
latestCompatibleWhatsNewDesc | str | The “what's new” description of the most recent compatible release (None if the plugin isn't in the plugin store) |
latestReleaseDate | datetime | The release date of the most recent release (None if the plugin isn't in the plugin store) |
latestRequiresIndigoVers | str | The Indigo release that is the minimum requirement of the most recent release (None if the plugin isn't in the plugin store) |
latestVers | str | The most recent release version (None if the plugin isn't in the plugin store) |
pluginDisplayName | str | The name displayed to users in the clients |
pluginFolderPath | str | The full path to the plugin file location (useful for creating a full path to files within the plugin bundle) |
pluginId | str | The ID of the plugin (same as was passed to the getPlugin() method above) |
pluginServerApiVersion | str | The max API version supported by the running Indigo Server |
pluginSupportURL | str | The URL supplied by the plugin that points to it's user documentation |
pluginVersion | str | The version number specified by the plugin |
storeIconURL | str | The URL to the plugin's icon in the plugin store (None if the plugin isn't in the plugin store) |
storeName | str | The name of the plugin in the plugin store (None if the plugin isn't in the plugin store) |
storePluginURL | str | The URL to the plugin in the plugin store (None if the plugin isn't in the plugin store) |
storeSummary | str | The description of the plugin in the plugin store (None if the plugin isn't in the plugin store) |
There are also a couple of methods defined by this object.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
executeAction(actionId, deviceId, props) | This is the method that actually executes the action. actionId is the unique action id. deviceId is the id of the device that the action on which the action will perform (if it requires a device). props is a dictionary of properties that the action needs to process correctly. See the plugin's documentation for a description of what you need to pass in to execute actions. |
isEnabled() | This method will return True if the plugin is enabled (running), False otherwise |
isInstalled() | This method will return True if the plugin is installed, False otherwise |
isRunning() | This method will return True if the plugin is running, False otherwise |
restart(waitUntilDone=True) | This method will restart the plugin if it's already running. Pass the optional parameter waitUntilDone=False if you don't want to block while the plugin restarts (waitUntilDone defaults to True if it's no parameters are passed). If you're a plugin developer and you want to restart the plugin from within itself you should pass that parameter. |
restartAndDebug(waitUntilDone=True) | The same as above, but it will restart in the debugger the user has selected in the Preferences. |
Plugin developers should test and document their plugin actions to make sure that the necessary information is available to scripters.
Examples
Restart a Plugin
There may be instances where you want to restart a plugin. This is how you do that from a script:
airfoil_id = "com.perceptiveautomation.indigoplugin.airfoilpro"
airfoil_plugin = indigo.server.getPlugin(airfoil_id)
if airfoil_plugin.isEnabled():
airfoil_plugin.restart()
Caveat: For safety reasons, we do not provide the ability to enable a plugin that is disabled, or disable a plugin that is enabled.
Check the documentation for each plugin for the necessary information and more examples.